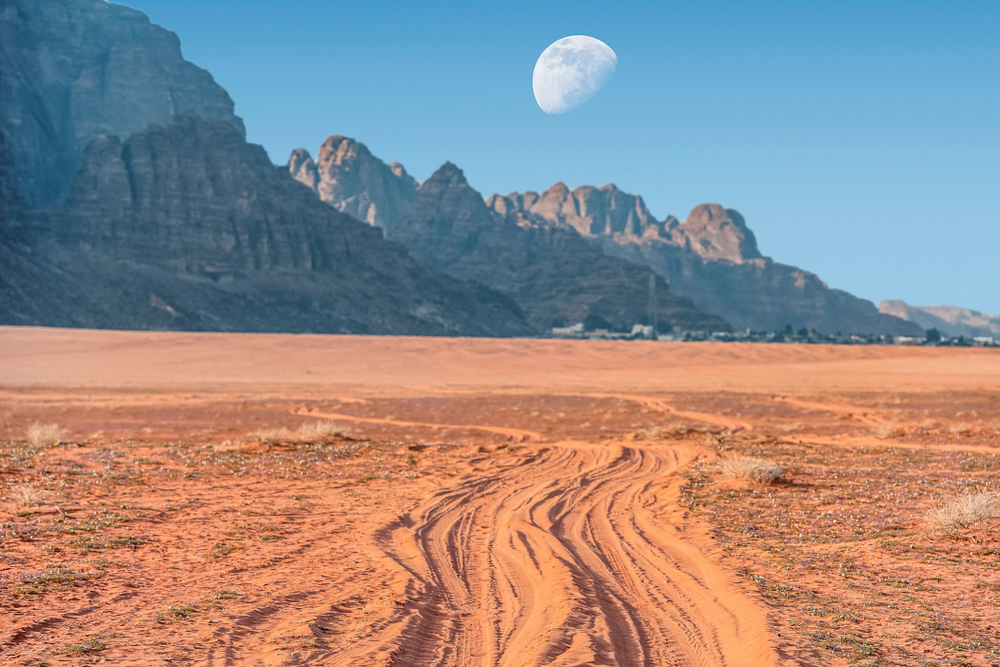




Jordan
Jordan (Arabic: الأردن; tr. Al-ʾUrdunn [al.ʔur.dunː]),
officially the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan (Arabic: المملكة
الأردنية الهاشمية; tr. Al-Mamlakah al-’Urdunniyyah
Al-Hāshimiyyah), is an Arab country in Western Asia, on the
East Bank of the Jordan River. Jordan is bordered by Saudi
Arabia to the south and the east, Iraq to the north-east,
Syria to the north and Israel and Palestine to the west. The
Dead Sea is located along its western borders and the
country has a 26-kilometre (16 mi) coastline on the Red Sea
in its extreme south-west.[7] Jordan is strategically
located at the crossroads of Asia, Africa and Europe.[8] The
capital, Amman, is Jordan's most populous city as well as
the country's economic, political and cultural centre.
What is now Jordan has been inhabited by humans since the
Paleolithic period. Three stable kingdoms emerged there at
the end of the Bronze Age: Ammon, Moab and Edom. Later
rulers include the Nabataean Kingdom, the Roman Empire, and
the Ottoman Empire. After the Great Arab Revolt against the
Ottomans in 1916 during World War I, the Ottoman Empire was
partitioned by Britain and France. The Emirate of
Transjordan was established in 1921 by the Hashemite, then
Emir, Abdullah I, and the emirate became a British
protectorate. In 1946, Jordan became an independent state
officially known as the Hashemite Kingdom of Transjordan,
but was renamed in 1949 to the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan
after the country captured the West Bank during the 1948
Arab–Israeli War and annexed it until it was lost to Israel
in 1967. Jordan renounced its claim to the territory in
1988, and became one of two Arab states to sign a peace
treaty with Israel in 1994. Jordan is a founding member of
the Arab League and the Organisation of Islamic
Co-operation. The sovereign state is a constitutional
monarchy, but the king holds wide executive and legislative
powers.
Jordan is a relatively small, semi-arid, almost landlocked
country with an area of 89,342 km2 (34,495 sq mi) and a
population numbering 10 million, making it the 11th-most
populous Arab country. Sunni Islam, practiced by around 95%
of the population, is the dominant religion and coexists
with an indigenous Christian minority. Jordan has been
repeatedly referred to as an "oasis of stability" in a
turbulent region. It has been mostly unscathed by the
violence that swept the region following the Arab Spring in
2010. From as early as 1948, Jordan has accepted refugees
from multiple neighbouring countries in conflict. An
estimated 2.1 million Palestinian and 1.4 million Syrian
refugees are present in Jordan as of a 2015 census.[3] The
kingdom is also a refuge to thousands of Iraqi Christians
fleeing persecution by ISIL. While Jordan continues to
accept refugees, the recent large influx from Syria placed
substantial strain on national resources and infrastructure.
Jordan is classified as a country of "high human
development" with an "upper middle income" economy. The
Jordanian economy, one of the smallest economies in the
region, is attractive to foreign investors based upon a
skilled workforce.[14] The country is a major tourist
destination, also attracting medical tourism due to its well
developed health sector.[15] Nonetheless, a lack of natural
resources, large flow of refugees and regional turmoil have
hampered economic growth.

Learn more about Jordan Here!